Manidipine
In today's world, Manidipine is a topic that arouses great interest and debate in different areas of society. Its relevance and diversity of approaches has led to extensive discussion and reflection on its implications. From academic perspectives to the everyday environment, Manidipine has generated endless questions and positions that seek to understand its scope and impact on our reality. In this article, we will delve into a detailed analysis of Manidipine, exploring its different aspects and offering a comprehensive vision to understand its importance and current challenges.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Manyper, Caldine, etc. |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C35H38N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 610.711 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Manidipine is a calcium channel blocker (dihydropyridine type) that is used clinically as an antihypertensive.
It was patented in 1982 and approved for medical use in 1990.
Synthesis
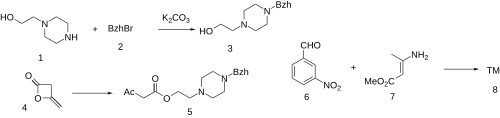
The alkylation between N-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine (1) and Benzhydryl Bromide (2) gives 2-(4-benzhydrylpiperazin-1-yl)ethanol (3). The reaction with Diketene (4) gives 2-(4-benzhydryl-1-piperazinyl)ethyl acetoacetate (5). The reaction with 3-nitrobenzaldehyde (6) and Methyl 3-aminocrotonate (7) completed the synthesis of Manidipine (8).
References
- ^ Cheer SM, McClellan K (2001). "Manidipine: a review of its use in hypertension". Drugs. 61 (12): 1777–1799. doi:10.2165/00003495-200161120-00010. PMID 11693466. S2CID 260814599. Archived from the original on 2013-01-17. Retrieved 2009-06-20.
- ^ McKeage K, Scott LJ (2004). "Manidipine: a review of its use in the management of hypertension". Drugs. 64 (17): 1923–1940. doi:10.2165/00003495-200464170-00011. PMID 15329044. S2CID 195689527. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2009-06-20.
- ^ Roca-Cusachs A, Triposkiadis F (2005). "Antihypertensive effect of manidipine". Drugs. 65 (Suppl 2): 11–19. doi:10.2165/00003495-200565002-00003. PMID 16398058. S2CID 25854593. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2009-06-20.
- ^ Otero ML (2007). "Manidipine-delapril combination in the management of hypertension". Vascular Health and Risk Management. 3 (3): 255–263. PMC 2293964. PMID 17703633.
- ^ Mizuno K, Haga H, Takahashi M, Fukuchi S (August 1992). "Evaluation of manidipine hydrochloride, a new calcium antagonist, in the treatment of hypertensive patients with renal disorders". Current Therapeutic Research. 52 (2): 248–253. doi:10.1016/S0011-393X(05)80475-8.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 465. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ Meguro, Kanji; Aizawa, Masahiro; Sohda, Takashi; Kawamatsu, Yutaka; Nagaoka, Akinobu (1985). "New 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives with potent and long-lasting hypotensive effect.". CHEMICAL & PHARMACEUTICAL BULLETIN. 33 (9): 3787–3797. ISSN 0009-2363. doi:10.1248/cpb.33.3787.
- ^ EP0094159 idem Kanji Meguro & Akinobu Nagaoka, US4892875 (1990 to Takeda Pharmaceutical Co Ltd).
- ^ Dharmaraj Ramachandra Rao, Rajendra Narayanrao Kankan, Maruti Ganpati Ghagare, WO20110203954 (2011 to Cipla Limited, Curtis, Philip Anthony).
- ^ 刘玉海, et al. CN105924382 (2018).
- ^ 金晓峰, et al. CN102875451 (2014 to CHANGZHOU PHARMACEUTICAL FACTORY CO LTD).
- ^ 刘忠春, CN107337632 (2017).
- ^ 谷志勇, et al. CN104292150 (2015).
- ^ , CN103351362 (2013 to).
- ^ http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZHOU200402000.htm