Kaʻala
In this article we will address the topic of Kaʻala, which has raised interest and debate in different areas. Since its emergence, Kaʻala has captured the attention of experts and fans alike, generating a wide variety of opinions and viewpoints. Over the years, Kaʻala has evolved and acquired a prominent place in today's society, influencing different aspects of daily life. In this article, we will analyze in depth the different aspects related to Kaʻala, as well as its impact in different areas. Furthermore, we will focus on the possible future implications of Kaʻala and the perspectives it offers for the future.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2013) |
| Kaʻala | |
|---|---|
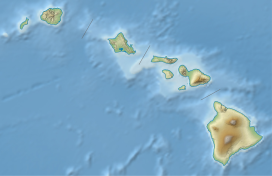
 Mt. Kaʻala, as seen from near Dole Plantation. | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 4,025 ft (1,227 m) |
| Prominence | 4,025 ft (1,227 m) |
| Coordinates | 21°30′25″N 158°08′34″W / 21.50694°N 158.14278°W |
| Naming | |
| Language of name | Hawaiian |
| Pronunciation | Hawaiian pronunciation: [kəˈʔɐlə] |
| Geography | |
| Location | Oahu, Hawaii, US |
| Parent range | Waianae Range |
| Topo map | USGS Haleiwa |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | 3.9 Ma |
| Mountain type | Plateau |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Hawaiian-Emperor seamount chain |
Kaʻala or Mount Kaʻala (pronounced [kəˈʔɐlə] in Hawaiian) is the highest mountain on the island of Oahu, at 1,227 metres (4,026 ft). It is a part of the Waianae Range, an eroded shield volcano on the west side of the island. The FAA maintains an active tracking station at the summit, which is closed to the general public and secured by the US Army which is stationed at the base of the mountain, at Schofield Barracks. The tracking station can be clearly seen from afar as a white, domed-shaped structure.
See also
- List of mountain peaks of the United States
- Evolution of Hawaiian volcanoes
- Hawaii hotspot
- Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain
References
- ^ "Mt. Mount Ka'ala". Department of Forestry and Wildlife. State of Hawaii. Retrieved 2013-02-21.
- ^ "Ka'ala". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2009-12-23.