Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout
Today we want to delve deeper into the topic of Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout, a topic that has gained relevance in recent years and that undoubtedly generates great interest among the population. Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout is a topic that covers multiple aspects and has been the subject of constant debate and analysis. In this article, we will explore different perspectives and approaches related to Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout, with the aim of providing a comprehensive view on this topic. From its origins to its impact today, Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout has captured the attention of academics, experts and the general public, being the object of study and interest in various areas. Without a doubt, Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout has become a relevant topic in contemporary society, which is why it is essential to deepen its understanding and scope.
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
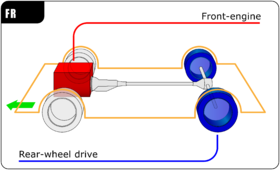
A front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout (FR) is an automotive design with an engine in front and rear-wheel-drive, connected via a drive shaft. This arrangement, with the engine straddling the front axle, was the traditional automobile layout for most of the 20th century. It is also used in trucks, pickups, and high-floor buses and school buses.
Front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout

A front mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout (FMR) places the engine in the front half of the vehicle but behind the front axle, which likewise drives the rear wheels via a driveshaft. Shifting the engine's center of mass rearward aids in front/rear weight distribution and reduces the moment of inertia, both of which improve a vehicle's handling.While the mechanical layout of an FMR is substantially the same as an FR car, the classification of some models of the same vehicle may vary as either FR or FMR depending on the length of the engine (e.g. 4-cylinder vs. 6-cylinder) and its center of mass in relation to the front axle.[citation needed]
FMR cars are often characterized by a long hood and front wheels that are pushed forward to the corners of the vehicle, close to the front bumper. 2+2-style grand tourers often have FMR layouts, as a rear engine does not leave much space for rear seats.
Gallery
-
The 390 cd V8 engine in a FR 1968 AMC AMX functionally straddles its front axle, with the centerline of the shock towers basically bisecting the center of the air cleaner
-
The straight-6 DOHC XK engine clearly sits behind the front axle of an FMR Jaguar E-Type
-
All Chevrolet Corvette from the second generation (model year 1963) through the seventh generation (model year 2019) are FMR. Only ancillary aspects of this Chevrolet Corvette ZR-1's engine may lie above the front axle.
-
An FMR Dodge Viper showing its 8.4l V10 positioned behind the car’s front axle
See also
References
- ^ "Development of a New Hybrid Transmission for RWD Car". www.sae.org. Archived from the original on 2009-02-07. Retrieved 2008-01-11.



